In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, the terms “cloud-based” and “web-based” applications are often used interchangeably, blurring the lines between their functionalities and nuances. However, understanding the distinctions between these two types of applications is essential for businesses aiming to leverage technology effectively. In this comprehensive analysis, we’ll delve into the core features, benefits, and use cases of both cloud apps and web apps, shedding light on their unique attributes and functionalities.
What is a Cloud Application?
A cloud application, also known as a cloud-based application, is a software program that operates in a cloud environment and is accessible through a local server. To grasp the concept of a cloud application fully, it’s crucial to understand the term “cloud” itself. In essence, the cloud refers to the internet, serving as a repository for remotely stored data. Cloud applications leverage this infrastructure to offer scalable and accessible solutions to users. Interested in harnessing the power of cloud technology for your next project? Discover how expert cloud development services can elevate your business to new heights.
Types of Cloud-based Applications
Cloud-based applications can be categorized into several types based on their functionality and data management approach:
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS): SaaS applications provide users with access to cloud-based software and IT infrastructure via a web browser. Examples include MS Office 365, Slack, and Salesforce CRM.
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS): PaaS applications enable users to create and manage their own applications using cloud-based platforms. Examples include Heroku and AWS Elastic Beanstalk.
Recovery as a Service (RaaS): RaaS applications focus on disaster recovery and data backup solutions for businesses, reducing downtime and ensuring data resilience.
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS): IaaS platforms offer backend management solutions, including servers, databases, and networks, accessible through a control panel. Examples include Microsoft Azure and Amazon AWS.
Benefits of Cloud Apps
Cloud applications offer numerous advantages over traditional software solutions, including:
Cost-effectiveness: Cloud apps follow a pay-per-usage model, reducing upfront costs and infrastructure expenses.
Enhanced scalability: Cloud apps can scale seamlessly to accommodate fluctuating user demands and business growth.
Improved collaboration: Cloud apps facilitate easy collaboration among remote teams through real-time data sharing and accessibility.
Automatic updates: Cloud service providers push regular updates to ensure security and performance enhancements without user intervention.
What is a Web Application?
In contrast to cloud apps, web applications are software programs designed to run on web browsers, relying entirely on web server frameworks for functionality. While web apps share similarities with cloud apps in terms of accessibility and scalability, they differ in their backend infrastructure and data processing approach.
Benefits of Web Apps
Web-based applications offer several benefits, including:
Accessibility: Web apps are accessible through any web browser on various operating systems, making them highly versatile and user-friendly.
Cost-effectiveness: Web apps eliminate the need for local installation and maintenance, reducing costs for both users and businesses.
Multi-user collaboration: Web apps support simultaneous access by multiple users, enabling seamless collaboration on shared projects and documents.
Simplified data processing: Web apps leverage remote web servers for data processing and storage, streamlining data management and ensuring data integrity.
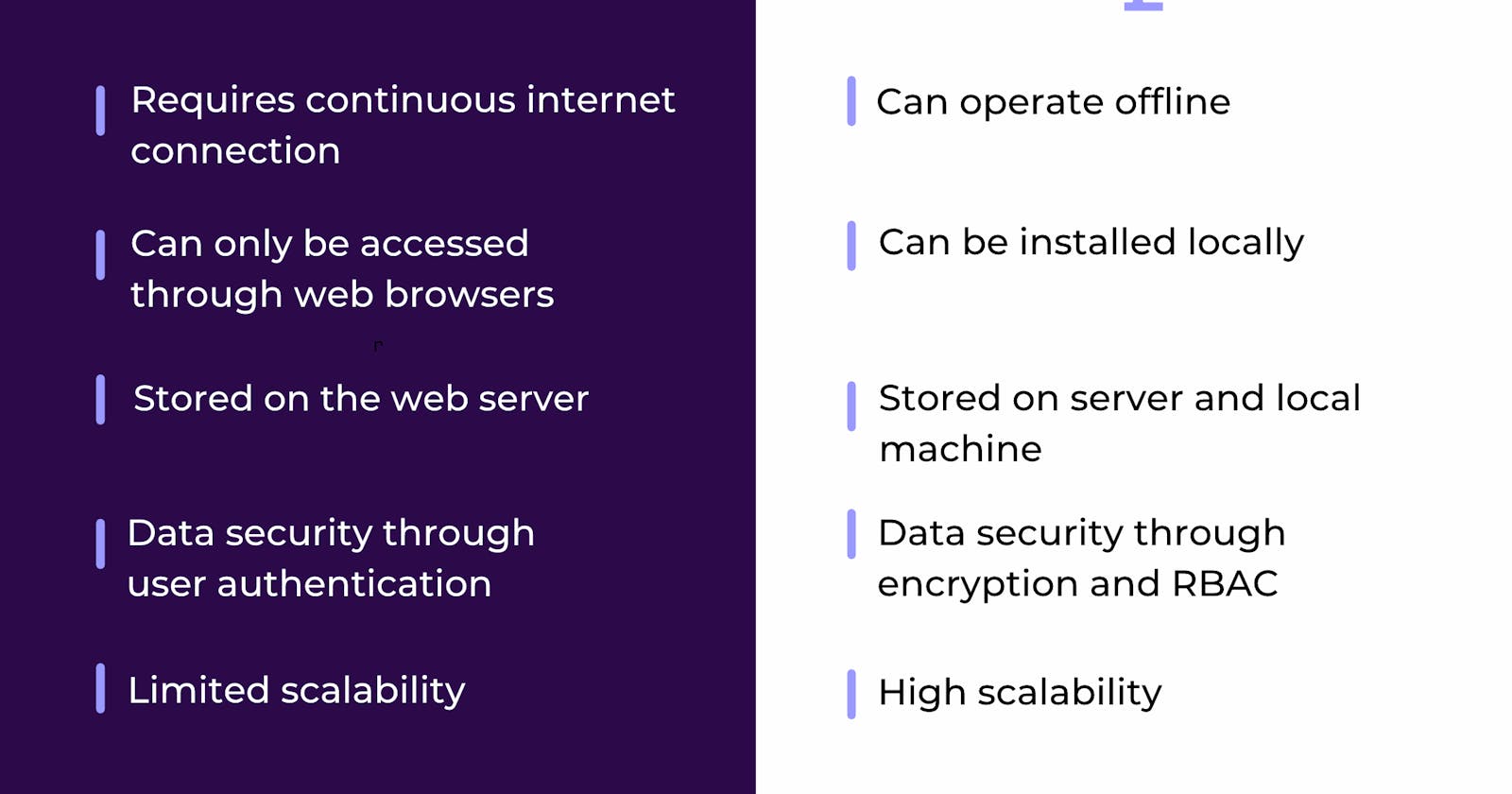
Cloud App vs Web App: Outlining the Contrasts
While both cloud-based and web-based applications share commonalities, they exhibit distinct differences in terms of architecture, dependency on web browsers, data security, and storage. Cloud apps, for instance, can function without an internet connection, while web apps rely on constant connectivity for data processing. Additionally, cloud apps offer advanced data security features, including encryption and role-based access control, compared to web apps.